- +91 - 9880470436
- info.anagha@gmail.com
Evaporative Cooling

Evaporative Cooling
An evaporative cooler (also swamp cooler, desert cooler, and wet air cooler) is a device that cools air through the simple evaporation of water. Evaporative cooling differs from air conditioning by refrigeration and absorptive refrigeration, which use vapor-compression or absorption refrigeration cycles. In the United States, the use of the term swamp cooler may be due to the odor of algae produced by early units.
Air washers and wet cooling towers use the same principles as evaporative coolers, but are optimized for purposes other than air cooling.
Temperatures Delivered By Evaporatives Coolers:
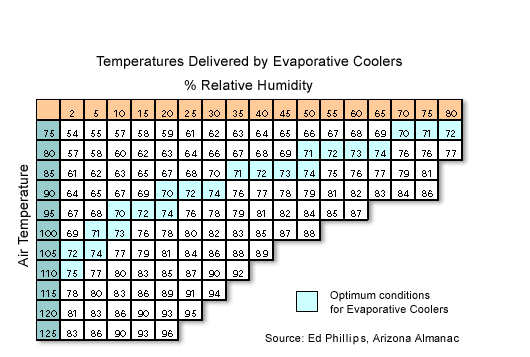
How Well Do Swamp Coolers Cool ?
The temperature of air coming out of an evaporative cooler obviously depends on the temperature and the humidity of the air going in. This chart from the Arizona Almanac shows that an evaporative cooler can deliver comfortable air under a wide variety of typical summertime temperature and humidity ranges.
In addition to the dropping the temperature of the air, evaporative cooling offers an additional cooling benefit. The constant movement of the air created by the blower - the cooling breeze it creates, if you will - makes the occupants of a room feel 4 to 6 degrees cooler than the actual temperature. This is the same effect you feel when you turn on a ceiling fan or a simple window fan. For this reason, the "effective temperature" created by an evaporative cooler will feel 4 to 6 degrees cooler than temperatures shown on the chart.
An added benefit of evaporative cooling is that it works best in the hottest time of the day. As the temperature outside increases as the sun climbs, the humidity normally drops. In the early morning, for example, the temperature may be 70 degrees, with a relative humidity of 60 percent. By mid-afternoon, when the temperature has climbed to 90 degrees, the humidity may well have dropped to 30 percent - conditions that make evaporative cooling work more effectively.
How to choose the right-sized evaporative cooler
For a swamp cooler to effectively cool, it must be the proper size for the job. A small portable unit, for example, will not adequately cool a large-sized room.
While the output of air conditioners are rated in BTUs (British Thermal Units), evaporative coolers are rated by CFMs (the cubic feet per minute of air that the cooler can blow into your home).
Whether it is for a single room or a whole house, there is a simple formula for determining the proper size of swamp cooler you need. Figure the cubic feet of space you want to cool, and then divide that number by two. The quotient will give you the CFM rating for the proper-sized swamp coolerFor example, if you have a 1,500 square foot home with 8 foot-high ceilings: 1,500 x 8 = 12,000 cubic feet 12,000 % 2 = 6,000 CFM needed
Benefits of Evaporative Cooling:
- Thanks to a new awareness of energy efficiency, evaporative coolers are achieving a new popularity. Remember, swamp coolers use as much as 75 percent less electricity as air conditioning does. The Sacramento Municipal Utility District estimates the electricity savings at approximately $150 a year. For hotter desert climates, the savings can be much more.
- Because the technology is simpler, an evaporative cooler costs about half as much as an air conditioner that will cool the same sized area. Some California utilities, such as PG&E, also offer rebates up to $300 to electricity customers who install whole-house evaporative systems. For perspective, a quick check of the internet in July 2001, found units capable of cooling 750 square feet that were priced as low as $275. Installation costs of swamp coolers are comparable to air conditioning units.
- Evaporative coolers operate on 120-volt electricity, which means they don't need special high-amperage circuits like many air conditioners do. A swamp cooler can be plugged into a nearby outlet.
- Many people appreciate the fact that evaporative cooling adds moisture to the air, which helps to keep wood furniture and fabrics from drying out. The moist pads through which the outside air flows are also fairly efficient air filters, trapping some dust and pollen. Since the pads are continually wetted, trapped particles are flushed out and trapped in the bottom of the cooler.
- Air conditioning works best when the windows are closed, since interior air is cooled and recirculated. Because swamp coolers cool outside air and blow it into the house, however, to work effectively they need at least one window open. The cooled outside air vents through open windows or doors, pushing out hot inside air and any smoke, odors and pollution that may be present. With evaporative cooling, a complete air change in a home occurs every one-to-three minutes. This flow of fresh air means that evaporative coolers can be operated without using the water pump to replace warm stale air with cooler nighttime air, much like a whole house fan does. That's an added benefit.
- Small evaporative coolers can be often placed in windows, much like a window air conditioner. This requires very little installation. Larger units usually require ducts to distribute the air, but these can be an existing forced air duct system in the house
- For the most part, evaporative cooling doesn't require as much ductwork as air conditioning. For a newly installed system, a short duct can direct the cooled air to a central point in the house. From there, air can be directed through the various rooms by simply opening and closing doors and windows to allow the cooled air to flow.

